Differential Diagnostics of Female Sexual Fluids a Narrative Review
| Bartholin's gland | |
|---|---|
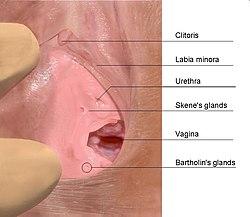 Female person genital organs with Bartholin's gland circled | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Urogenital sinus |
| Artery | external pudendal artery[i] |
| Nervus | ilioinguinal nerve[1] |
| Lymph | superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | glandula vestibularis major |
| MeSH | D001472 |
| TA98 | A09.2.01.016 |
| TA2 | 3563 |
| FMA | 9598 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
The Bartholin's glands (named subsequently Thomas Bartholin; too called Bartholin glands or greater vestibular glands) are 2 pea sized compound alveolar glands[ii] located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina. They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina and are homologous to bulbourethral glands in males. However, while Bartholin's glands are located in the superficial perineal pouch in females, bulbourethral glands are located in the deep perineal pouch in males. Their duct length is 1.five to 2.0 cm and they open up into navicular fossa.[2] The ducts are paired and they open on the surface of the vulva.
History [edit]

De ovariis mulierum et generationis historia epistola anatomica, 1678
Bartholin's glands were kickoff described in the 17th century by the Danish anatomist Caspar Bartholin the Younger (1655–1738).[three] [4] Some sources mistakenly ascribe their discovery to his grandpa, theologian and anatomist Caspar Bartholin the Elder (1585–1629).[5]
Function [edit]
Bartholin's glands secrete mucus to provide vaginal lubrication during sexual arousal.[4] [half dozen] [7] The fluid may slightly moisten the labial opening of the vagina, serving to make contact with this sensitive area more comfortable.[8] Fluid from the Bartholin'south glands is combined with other vaginal secretions equally a "lubrication fluid" in the amount of well-nigh 6 grams per solar day, and contains high potassium and low sodium concentrations relative to blood plasma, with a slightly acidic pH of iv.7.[9]
Clinical pathology [edit]
Information technology is possible for the Bartholin'due south glands to get blocked and inflamed resulting in pain.[8] This is known as bartholinitis or a Bartholin's cyst.[4] [10] [11] A Bartholin'due south cyst in turn can become infected and form an abscess. Adenocarcinoma of the gland is rare and beneficial tumors and hyperplasia are fifty-fifty more rare.[12] Bartholin gland carcinoma is a rare malignancy that occurs in ane% of vulvar cancers. This may be due to the presence of three different types of epithelial tissue.[three] Inflammation of the Skene'south glands and Bartholin glands may appear like to cystocele.[13]
Come across also [edit]
- Skene's gland
References [edit]
- ^ a b Greater Vestibular (Bartholin) gland Archived January 12, 2007, at the Wayback Auto
- ^ a b Manual of Obstetrics. (tertiary ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1-16. ISBN 9788131225561.
- ^ a b Heller, Debra S.; Bean, Sarah (2014). "Lesions of the Bartholin Gland". Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease. eighteen (4): 351–357. doi:x.1097/LGT.0000000000000016. ISSN 1089-2591. PMID 24914884.
- ^ a b c Lee, M. Y; Dalpiaz, A; Schwamb, R; Miao, Y; Waltzer, W; Khan, A (2015). "Clinical Pathology of Bartholin'south Glands: A Review of the Literature". Current Urology. 8 (1): 22–25. doi:x.1159/000365683. PMC4483306. PMID 26195958.
- ^ C. C. Gillispie (ed.): Dictionary of Scientific Biography, New York 1970.[ page needed ].
- ^ "Viscera of the Urogenital Triangle". University of Arkansas Medical School. Archived from the original on 2010-01-xviii. Retrieved 2007-07-23 .
- ^ Chrétien, F.C.; Berthou J. (September 18, 2006). "Crystallographic investigation of the dried exudate of the major vestibular (Bartholin'due south) glands in women". Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 135 (1): 116–22. doi:ten.1016/j.ejogrb.2006.06.031. PMID 16987591.
- ^ a b "Bartholin'southward Gland". Discovery Wellness. Archived from the original on 2008-08-04.
- ^ Pastor Z, Chmel R (2017). "Differential diagnostics of female person "sexual" fluids: a narrative review". International Urogynecology Journal. 29 (5): 621–629. doi:x.1007/s00192-017-3527-9. PMID 29285596. S2CID 5045626.
{{cite periodical}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Sue East. Huether (2014). Pathophysiology: The Biologic Basis for Affliction in Adults and Children. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 817. ISBN9780323293754.
- ^ Lee, William A.; Wittler, Micah (2020), "Bartholin Gland Cyst", StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30335304, retrieved 2020-03-24
- ^ Argenta PA, Bell K, Reynolds C, Weinstein R (Oct 1997). "Bartholin'due south gland hyperplasia in a postmenopausal woman". Obstetrics & Gynecology. ninety (4 part 2): 695–7. doi:10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00409-2. PMID 11770602. S2CID 8403143.
- ^ "Cystoceles, Urethroceles, Enteroceles, and Rectoceles - Gynecology and Obstetrics - Merck Manuals Professional Edition". Merck Manuals Professional Edition . Retrieved 2018-02-06 .
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bartholin%27s_gland
0 Response to "Differential Diagnostics of Female Sexual Fluids a Narrative Review"
Post a Comment